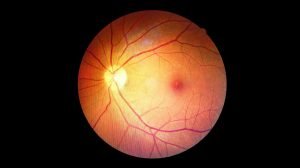
When diagnosed with Diabetic Retinopathy, one of the biggest questions patients and their families ask is: “How will I be treated?” Fortunately, with advances in ophthalmic medicine, there are many effective treatment methods for diabetic retinopathy that help control the disease, prevent vision loss, and preserve quality of life.
This article will delve into the most modern treatment options available today, helping you understand each method, when it’s indicated, and what you can expect on your treatment journey.
Goals of Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment: More Than Just a “Cure”
It’s important to understand that diabetic retinopathy is a chronic complication of diabetes. The primary goals of treatment are not a complete “cure” (as severe damage often cannot be fully reversed), but rather to:
- Prevent or slow down the progression of the disease.
- Reduce diabetic macular edema (DME) to improve or maintain central vision.
- Control the growth of abnormal blood vessels and prevent bleeding.
- Preserve existing vision and prevent permanent vision loss.
To achieve these goals, a combination of treatment methods is often necessary, starting with the strongest foundation.
>> Common Retinal Diseases and Effective Prevention Methods
The Most Important Foundation: Systemic Diabetes Control
Regardless of the specific eye treatment applied, rigorous control of blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol remains the key factor determining the long-term success of diabetic retinopathy treatment.
- Stable Blood Sugar: Helps slow down the process of retinal blood vessel damage.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol within Safe Limits: Reduces strain on the vascular system, preventing atherosclerosis and blockages.
While not a direct eye treatment, this systemic control is a prerequisite for other eye treatments to be maximally effective.
Specific Eye Treatment Methods
When diabetic retinopathy has caused significant damage or is at high risk of progression, your ophthalmologist will recommend specific treatment methods.
Intravitreal Injections
This is one of the most common and effective treatment methods currently available, particularly for diabetic macular edema (DME) and proliferative stages of the disease.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Anti-VEGF Drugs: Medications like Ranibizumab, Aflibercept, and Bevacizumab work by inhibiting Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF). VEGF is a protein that causes the growth of abnormal new blood vessels (neovascularization) and increases blood vessel permeability, leading to fluid leakage and swelling. By blocking VEGF, these drugs help reduce swelling and regress abnormal vessels.
- Corticosteroids: In some cases, intraocular corticosteroids (e.g., Dexamethasone implant, Fluocinolone acetonide implant) may be injected into the eye to reduce inflammation and macular edema.
- Injection Procedure: After applying numbing eye drops, the doctor will inject a tiny amount of medication directly into the vitreous cavity of the eye. The procedure is quick, usually painless, and performed in a sterile environment.
- Number of Injections: Often requires multiple repeated injections (following a monthly or spaced-out protocol) to maintain effectiveness, depending on the individual patient’s response and the disease’s severity.
- Effectiveness and Side Effects: Highly effective in improving vision affected by macular edema and inhibiting new vessel growth. Side effects are usually mild, such as temporary redness or discomfort, but serious complications like infection are rare.
Laser Photocoagulation Treatment
Laser therapy has been widely used for decades to treat diabetic retinopathy, helping to “burn” or “seal off” abnormal blood vessels.
- Focal/Grid Laser:
- Indication: Used for localized diabetic macular edema.
- Mechanism: Laser beams are aimed at specific leaking blood vessels in the macular area to seal them, helping to reduce swelling and improve central vision.
- Panretinal Photocoagulation (PRP):
- Indication: Used for proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) with the growth of new blood vessels.
- Mechanism: The doctor uses a laser to create hundreds of tiny burns on the peripheral retina. The goal is to reduce the oxygen demand of the ischemic (oxygen-deprived) retinal areas, thereby inhibiting the growth of dangerous new blood vessels and preventing hemorrhage and the risk of retinal detachment.
- Advantages: Effective in preventing the disease from worsening.
- Limitations: May cause some loss of peripheral vision or night vision, but this trade-off is accepted to protect central vision and prevent more severe vision loss.
Vitrectomy Surgery
This surgical procedure is performed when diabetic retinopathy has progressed to a very severe stage, and other methods are no longer effective.
- Indications:
- Severe Vitreous Hemorrhage: When blood fills the vitreous cavity, severely obstructing or eliminating vision.
- Tractional Retinal Detachment: When scar tissue formed by new blood vessels contracts and pulls the retina away from its normal position.
- Persistent Macular Edema unresponsive to other treatments.
- Procedure: The surgeon makes a few tiny incisions in the eye, using micro-instruments to remove the blood-filled vitreous or scar tissue. The vitreous cavity may then be refilled with a saline solution, gas, or silicone oil to hold the retina in place.
- Recovery: Vitrectomy typically requires a certain recovery period and strict adherence to the doctor’s post-operative instructions.
Choosing the Right Treatment for Diabetic Retinopathy
The choice of the most suitable diabetic retinopathy treatment method will be made by your ophthalmologist based on several factors:
- Stage and severity of the disease: NPDR or PDR, presence of macular edema, presence of hemorrhage or retinal detachment.
- Patient’s overall health status: Co-existing medical conditions, ability to respond to medication or surgery.
- Current vision and patient expectations.
- Condition of the other eye.
Your doctor will clearly explain the pros and cons of each method, success rates, potential risks, and the long-term treatment plan. Always ask questions and discuss openly with your doctor to make the best decision together.
Post-Treatment Follow-up and Long-Term Disease Management
Successful treatment does not mean the disease has disappeared. Diabetic retinopathy is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management.
- Regular Follow-up Appointments: Crucial for monitoring the response to treatment, detecting any recurrence or progression of the disease early.
- Strict Control of Blood Sugar, Blood Pressure, and Cholesterol: Continuously and rigorously. This remains the most important factor in maintaining treatment effectiveness and preventing new damage.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Balanced diet, regular exercise, no smoking.
Frequently Asked Questions About Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment (FAQ)
Q1: Do intravitreal injections hurt?
A1: The injection process is usually painless thanks to numbing eye drops. You might feel a slight pressure or mild discomfort for a few seconds. After the injection, your eye may feel a bit gritty or appear slightly red, but this usually subsides within a few days.
Q2: Will my vision return to normal after laser treatment?
A2: The goal of laser treatment is to halt disease progression and preserve vision. It can help improve vision if macular edema is controlled. However, it cannot completely reverse retinal damage that occurred previously.
Q3: Are there risks associated with vitrectomy surgery?
A3: Like any surgery, vitrectomy carries certain risks such as infection, bleeding, recurrent retinal detachment, or cataract formation. However, with modern techniques, the success rate is quite high, and serious complications are rare.
Q4: Is the cost of diabetic retinopathy treatment high?
A4: Treatment costs depend on the method prescribed, the number of injections or surgeries, and the medical facility. Early detection and treatment are often less expensive and lead to better outcomes than treating the disease at an advanced stage.
Q5: How long does it take to see results after treatment?
A5: Treatment effectiveness can vary depending on the method and individual patient. With intravitreal injections, some people may see improvement within a few weeks. With laser, stable effects might take a few months. Your doctor will monitor you closely and inform you about your progress.
>> Read more: Macular Hole: Signs, Causes, Diagnosis & Effective Treatment
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy presents a significant challenge for individuals with diabetes, but it can be effectively managed and controlled through advanced treatment methods.
The most crucial aspect is the collaboration between the patient and the doctor, along with adherence to the treatment plan and rigorous control of systemic diabetes. Do not hesitate to seek professional consultation. Contact European Eye Center for an examination and advice from leading specialists, helping you choose the optimal treatment solution for your eyes.