Living with diabetes means you’re constantly managing your health. Beyond concerns like your heart or kidneys, there’s a silent yet formidable threat you cannot ignore: diabetic retinopathy. This is the leading cause of permanent vision loss in people with diabetes, and alarmingly, it often progresses without any clear symptoms until it’s too late.
Don’t let complacency cost you your precious sight. This article will help you understand this threat, explaining why regular eye exams are not just a recommendation but a crucial prerequisite to protect your eyes and maintain your quality of life.
How Does Diabetes Affect Your Eyes? (Diabetic Retinopathy Explained)
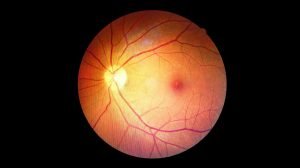
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a serious complication that occurs when persistently high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels nourishing the retina. The retina, a light-sensitive nerve tissue at the back of your eye, plays a vital role in capturing images and sending signals to your brain, allowing us to see.
When these retinal blood vessels are damaged, they can cause a range of problems, progressing through stages:
- Early Stage (Non-Proliferative DR – NPDR): Blood vessels weaken, swell into tiny bulges (microaneurysms), and leak fluid or blood. If this fluid accumulates in the macula (the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, detailed vision), it causes Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), leading to blurred or distorted central vision.
- Advanced Stage (Proliferative DR – PDR): The retina becomes severely deprived of oxygen, triggering the formation of new, abnormal blood vessels. These new vessels are extremely fragile and prone to breaking, causing significant bleeding into the eye (vitreous hemorrhage) that leads to sudden, severe vision loss. Scar tissue can also form with these abnormal vessels, pulling the retina away from its normal position (tractional retinal detachment)—an emergency condition that can cause permanent blindness if not treated promptly.
Beyond high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and the duration of diabetes are also significant risk factors that increase the likelihood and severity of diabetic retinopathy.
Warning Signs of Diabetic Retinopathy to Watch For
One of the biggest challenges with diabetic retinopathy is its typically asymptomatic nature in the early stages. You might have 20/20 vision, yet your retina could already be sustaining damage. This is why many patients become complacent, only seeking help when their vision has severely deteriorated.
However, as the disease progresses, you might start noticing these warning signs in one or both eyes:
- Blurred or fluctuating vision: Your ability to see details clearly may diminish, or your vision may change erratically throughout the day.
- Sudden increase in floaters: You may see more “black spots,” “cobwebs,” or “specks” drifting in your vision, especially noticeable against a bright background.
- Flashes of light: Occasional fleeting flashes of light in your peripheral vision.
- Difficulty seeing in dim light or at night.
- Blind spots or dark areas: A part of your visual field might be obscured by a “gray curtain” or a dark patch.
- Distorted or wavy vision: Especially if the macula is affected, straight lines might appear bent or wavy.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek an eye doctor immediately. This could be an urgent signal from your eyes.
Why Are Regular Eye Exams Critical for Diabetics?
Regular eye exams are your “golden key” to protecting your vision as a diabetic. They are the sole and most effective method for detecting damage early, before it becomes severe, allowing your doctor to intervene promptly:
- Early detection, prevent damage: Even with 20/20 vision, an ophthalmologist can spot the subtlest changes in your retina using specialized equipment. Early detection helps prevent the disease from progressing or at least slows down the damage process.
- More effective treatment: Modern treatments like laser photocoagulation and intraocular injections (anti-VEGF) are most effective when performed in the early stages of the disease, helping to preserve or even restore some vision.
- Monitoring and adjusting treatment plans: Regular exams help your doctor monitor the condition of your retina, assess the effectiveness of your blood sugar control, and recommend lifestyle adjustments or treatment modifications as needed.
- Prevent permanent vision loss: Skipping regular exams can lead to the disease advancing to an irreversible stage, resulting in permanent blindness.
>> Read more: How to Read Your Eyeglass Prescription: A Simple Guide from A to Z
Recommended Eye Exam Frequency:
- Type 1 Diabetes Patients: First eye exam within 5 years of diagnosis, then at least once a year.
- Type 2 Diabetes Patients: First eye exam immediately upon diagnosis, then at least once a year.
- Pregnant women with diabetes: Should have an eye exam before or during the first trimester of pregnancy and be monitored more closely as advised by their doctor.
- Any diabetic patient experiencing unusual eye symptoms should seek immediate examination, without waiting for their scheduled appointment.
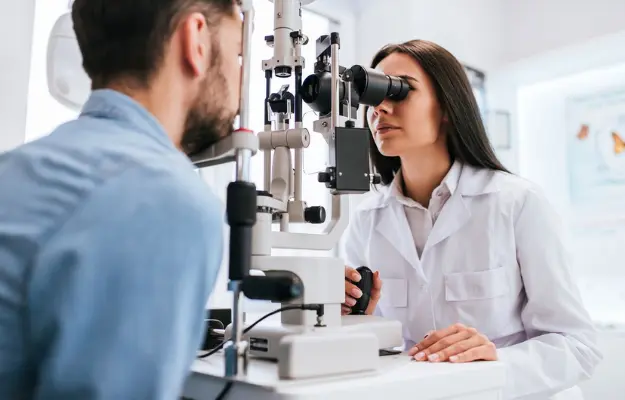
The Specialized Diabetic Eye Exam Process
A comprehensive eye exam for diabetic patients is designed to thoroughly evaluate your overall eye health, with a particular focus on the retina. The process is typically quick, painless, and non-invasive:
- Vision and Eye Pressure Test: Your doctor will check your visual acuity and measure the pressure inside your eye to screen for glaucoma, another eye condition with a higher risk in diabetic individuals.
- Pupil Dilation: This is a crucial step. Specialized eye drops will be administered to widen your pupils. This allows the doctor a clear and comprehensive view of your retina and its delicate blood vessels.
- Fundoscopy (Retinal Examination): Using a slit lamp microscope and specialized lenses, the doctor will meticulously examine your retina, macula, optic disc, and blood vessels. They will look for signs of damage like microaneurysms, hemorrhages, leakage, blockages, or the formation of abnormal blood vessels.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This advanced, non-invasive imaging technique provides high-resolution cross-sectional images of your retina. OCT is incredibly useful for accurately detecting macular edema (swelling of the macula) or even the smallest structural changes in the retina that might be missed during a standard exam, greatly aiding diagnosis and monitoring treatment effectiveness.
- Fluorescein Angiography (FA) (if necessary): In some specific cases, your doctor may recommend injecting a special dye into a vein in your arm. This dye travels to your eyes and highlights blood flow in the retinal vessels, helping to precisely identify leaking, blocked, or abnormal new vessels.
Important Post-Exam Note: Your vision will likely be blurry and light-sensitive for several hours due to the dilating eye drops. Please arrange for a friend or family member to drive you home after your appointment for your safety.
Comprehensive Diabetes Management
Regular eye exams are an essential shield, but they are only part of the solution. To optimally protect your vision from diabetic retinopathy, you must integrate them with comprehensive management of your diabetes:
- Strict Blood Sugar Control: This is the most critical factor. Maintaining stable blood sugar levels close to your personalized targets (measured by HbA1c) will significantly slow down or prevent retinal damage.
- Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Management: High blood pressure and high cholesterol also severely damage blood vessels, increasing the risk and severity of diabetic retinopathy. Follow your treatment plan to keep these levels within a healthy range.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet rich in greens and fruits, while limiting sugar, salt, and saturated fats. Regular exercise helps control blood sugar and blood pressure.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking dramatically increases the risk of blood vessel damage and accelerates the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
- Adhere to Treatment Plans: Take your diabetes medication and any other prescribed medications exactly as directed by your endocrinologist and ophthalmologist.
How to Protect Your Vision Today
Diabetic retinopathy is a very real threat, but it’s one you can proactively manage. Regular eye exams are the essential action to detect it early, treat it promptly, and preserve your precious sight.
Don’t wait until symptoms appear and your vision begins to decline. Make annual eye exams an indispensable priority in your health management plan. This action will not only help you maintain your vision but also enhance your quality of life, allowing you to confidently see all the beauty of the world and your future.
If you are a diabetic patient due for an eye exam, or if you have any concerns about your vision, do not hesitate. Contact European Eye Center today to schedule your comprehensive diabetic eye examination. Our team of experts is dedicated to providing European-standard eye care that is meticulous, caring, and professional, ensuring your peace of mind regarding your eye health.